The Step-By-Step Approach to Better Blood Sugars: Walking
If you’re like me, you might have a health-focused New Year’s resolution posted on your wall: "lose weight," "exercise more, "be less stressed."
Unfortunately, making resolutions is easy, but sticking to them is hard. A 15,000-person survey found that four out of five people who make New Year’s resolutions eventually break them. And it gets worse: a sizeable percentage of people (11%) in one survey actually broke their resolution one week in!
As I pondered this depressing data, I thought about scientifically testing the simplest, most fundamental exercise possible: walking. It can be done anywhere, does not cost anything, and requires no equipment. And because the barriers to doing it are so low, it also helps address that very basic New Year’s Resolution conundrum outlined above. What follows is my personal diabetes experience testing the blood sugar benefits of walking, a brief review of studies on diabetes and walking, and five tips to incorporate walking into your daily routine.
If you find this article useful, check out my upcoming book, Bright Spots & Landmines!
Walking with diabetes – my own experience
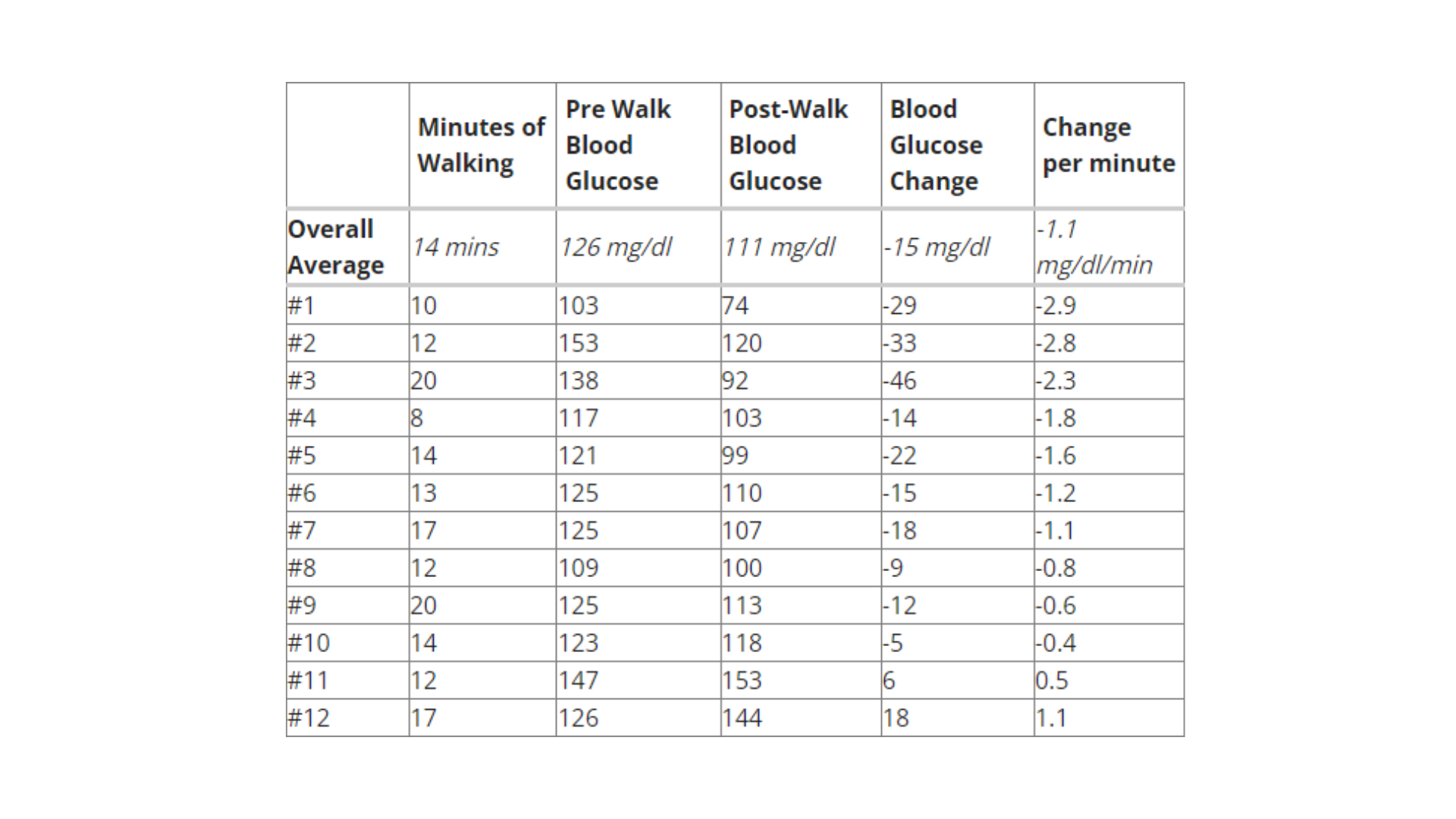
As a fitness fiend my whole life, I tend to think of “exercise” with a very intense, all-or-nothing frame of reference: cycling, strength training, and playing basketball. So when I approached the question of how much walking could really drop my blood sugars, I was skeptical. In an effort to test it objectively, I performed a dozen periods of walking, and measured my blood glucose immediately before and immediately after finishing. I timed each walk with a stopwatch, always made sure I had less than one unit of insulin-on-board, and tried to go at a normal speed.
On average, walking dropped my blood sugar by approximately one mg/dl per minute. The largest drop I saw was 46 mg/dl in 20 minutes, more than two mg/dl per minute. Walking was also surprisingly effective: my blood sugar dropped in 83% of my tests. There were only two times where I did not see a drop in blood sugar; in these instances, I suspect it was either blood glucose meter inaccuracy or a delayed blood glucose rise from meals (e.g., fiber, fat) that contributed to the increase. Those interested can see the complete table of my walking endeavors at the end of this article.
Some might argue that one mg/dl per minute is not very impressive, but the key for me is reducing my insulin intake. One unit of insulin tends to drop my blood glucose by 25 mg/dl (morning) and 35 mg/dl (afternoon and evening). My rapid-acting insulin (Novolog) takes about 60-90 minutes to peak and three hours to completely finish working, meaning any drop in blood glucose takes a while. With a blood sugar of 170 mg/dl, I could either take two units of insulin and wait well over an hour for my blood glucose to really drop, or I could walk for a little more than 30-40 minutes. I found it liberating that something as simple and easy as walking could be a replacement for (or augment to) taking insulin.

I originally had hoped to test the effects of walking after meals but found it hard to do a thoroughly scientific job of it. What I can say, however, is that walking after meals definitely lowered my insulin requirements. Generally, planning a post-meal walk of around 20 minutes meant I needed about half as much insulin as normal, and in some cases no insulin at all. The caveat is that I do tend to eat pretty low carbohydrate meals, so those eating higher carb meals may find their needs differ. The best way to see how walking affects your blood sugar it to try it for yourself.
What does the research say about walking with diabetes?
I found many published studies on walking with diabetes, and most showed a benefit. I’ve categorized them below into type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and prediabetes/overweight/obese. The list below is not exhaustive by any stretch, but I hope it gives a broad sense of some of the scientific research supporting the benefits of walking.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A 2012 study of 201 people with type 2 diabetes found that every additional 2,600 steps of walking each day was associated with a 0.2% lower A1c. For reference, 2,600 steps is a little over a mile (about 20 minutes walking at a normal pace). In an interesting 2005 study of 179 patients with type 2 diabetes, medication costs, insulin usage, and physical activity were tracked over a two-year period. Over that time, taking a three-mile daily walk (about an hour per day) was estimated to reduce drug costs by $550 and other medical costs by $700. The number of patients on insulin therapy also fell by a compelling 25%. And a small 2012 study examined the emotional effects of walking in individuals with type 2 diabetes – in the 16 patients that participated in the study, 20 minute walks were associated with significant positive influences on psychological well-being.
- Type 1 Diabetes: Though few studies have tested walking in people with type 1 diabetes, the results do seem positive, particularly after meals. A 2012 study examined 12 patients with type 1 diabetes over 88 hours. Those who walked after meals had approximately one half the glucose excursion compared to those who did not walk after meals. Interestingly, the same study found a similar glycemic benefit in those without diabetes. The researchers concluded, “Walking significantly impacts postprandial [after meal] glucose excursions in healthy populations and in those with type 1 diabetes.”
- Prediabetes/Overweight/Obese: A 2007 analysis, which included five studies examining walking and the risk of type 2 diabetes (data from a staggering 301,221 people), found that those who walked regularly (about 20 minutes per day) had a 30% lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared to those who did almost no walking at all. A 1999 analysis of the Nurses Health Study also examined the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, this time in over 70,000 female nurses over an eight-year period. Walking was strongly associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes, and the speed was important – compared to those who walked at an “easy pace” (longer than 30 minutes to walk one mile), those who walked at a “normal” pace (20-30 minutes per mile) had a 14% lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Walking at a brisk pace (faster than 20 minutes per mile) was linked with a 41% lower risk of type 2 diabetes.
How can I incorporate walking and other types of exercise into my daily routine?
1. Take it one step at a time: A good way to start something new is to take it slow, set achievable goals, and then make them more ambitious over time. If you don’t walk at all right now, make a goal to walk one minute per day. Next week, walk two minutes per day. Starting small and building up over time makes starting a new goal less daunting. Plus, the gains you make will give you a sense of satisfaction and encourage you to keep going.
2. Make a schedule: One easy way to remind yourself to walk or exercise is to schedule it on your calendar – this can serve as a daily reminder, as well as a way to protect that time and avoid overscheduling yourself. And if your goal is 100 minutes of walking per week, a calendar can make it seem manageable: just 15 minutes per day.
3. Involve friends and family: Having someone join you in an exercise program can help keep you accountable (i.e., you may be less likely to skip out on a session if you know you’d be letting your partner down), make the time pass more quickly, and even help foster some healthy competition.
4. Make it fun: To pass the time while walking, I’ve become a huge fan of listening to audiobooks, music, or calling family members. There are also a variety of smartphone apps that are designed to make walking more fun, trackable over time, and even more competitive. I'm a big fan of activity trackers like Fitbit, which can be very motivating for increasing daily steps.
5. Sneak it in: If you’re not into planning exercise, there are still cool and easy ways to get more walking in. You can park farther away when you go to the store, take the stairs instead of the elevator or escalator, and take walking breaks with colleagues at work – the latter is a diaTribe staff favorite to enjoy the beautiful Lower Haight neighborhood here in San Francisco.
Credited: [Author:
Adam Brown], [Source: diaTribe Learn MAKING SENSE OF DIABETES], [Site: https://diatribe.org/]
Healthy Bites