Noticias

With Mother’s Day around the corner, now’s the time to find the perfect gift. From foot massagers and Fitbits to diabetes-friendly treats, our gift guide has something for every mom. Looking to show your mom or another MWD (mom with diabetes) how much you appreciate them? Rest easy – diaTribe has hand-picked 12 great diabetes gifts for Mother’s Day. To make sure these presents pass the all-important reality check, we consulted some MWDs in the know, including Jennifer Smith. Working primarily with women as the director of lifestyle and nutrition at Integrated Diabetes Services, Smith has type 1 diabetes and is a mother of two boys. What is her key to nailing a Mother's Day gift for someone with diabetes? “You have to know the person,” said Smith. “And the gift might have nothing to do with diabetes.” If you want even more selection, check out diaTribe’s roundup of thoughtful gifts for people with diabetes . Or, just get scrolling.
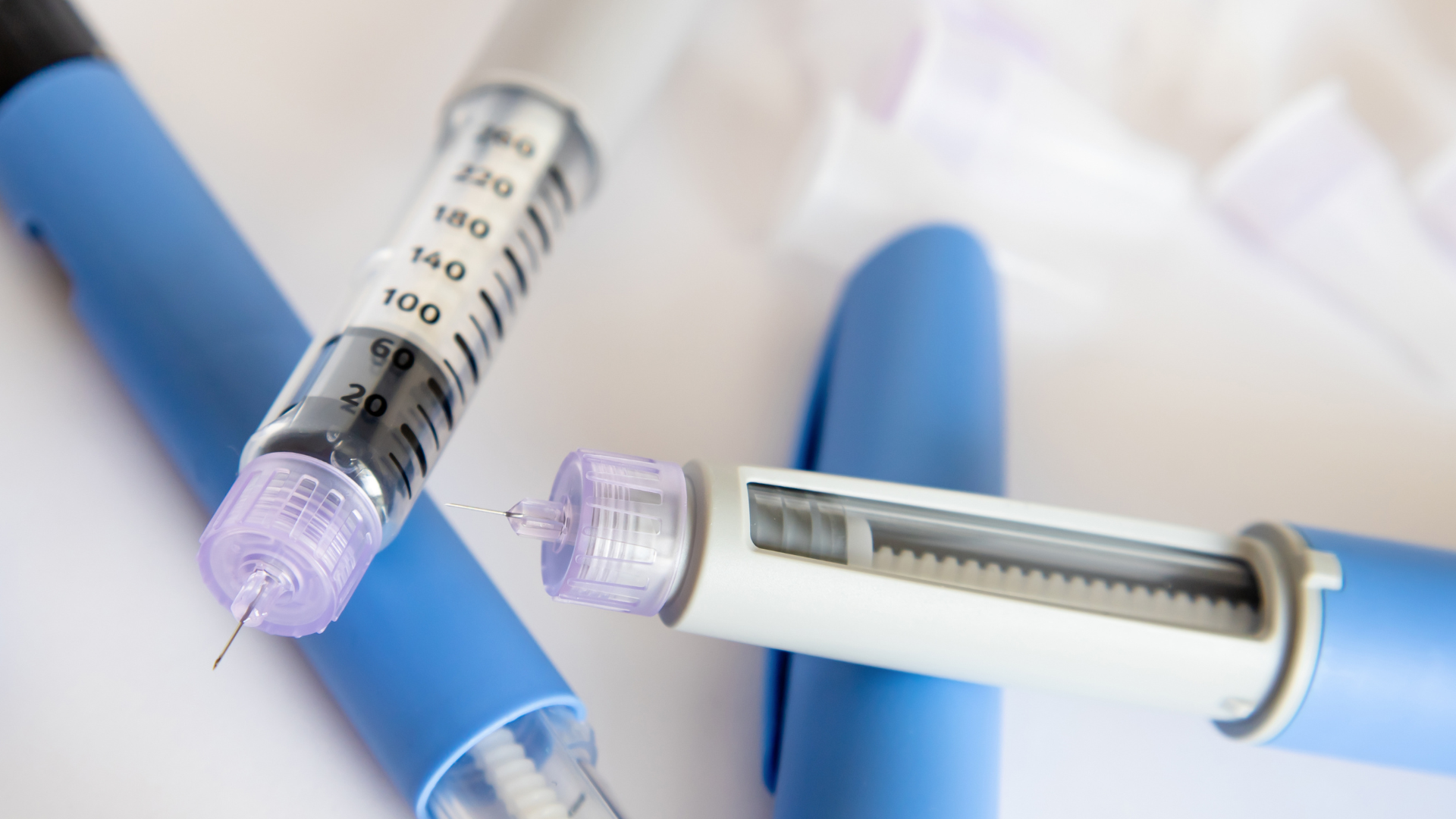
Whether you use syringes or insulin pens, injections can be a pain – literally. Here are techniques and tips to make injections as seamless as possible. There are many ways to take insulin , including syringes, prefilled pens, or insulin pumps. How you take insulin is highly personal – different people have different dosage needs, timing, and preferences. If you take insulin through injections, it’s important to choose and rotate injection sites properly and follow recommended steps to ensure safety. For the first time since 2016, experts from the Forum for Injection Technique and Therapy Expert Recommendations (FITTER) have updated recommendations on how to inject insulin correctly. Here, we cover the key updates and offer helpful tips to make injections a breeze.
Type 2 diabetes, a condition marked by chronically high blood sugar levels, is a leading driver of metabolic disease in America. While conventional medical advice recommends taking medications to control blood sugar levels, this is only a temporary measure at best. Diabetes is compounded by several factors, and recent research notes that nutritional deficiencies is a commonly overlooked aspect, and that when these deficiencies are addressed, managing and controlling this disease becomes easier.








